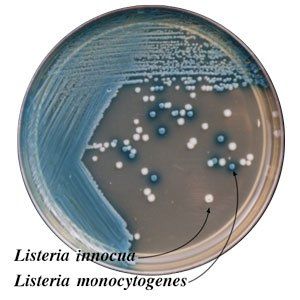
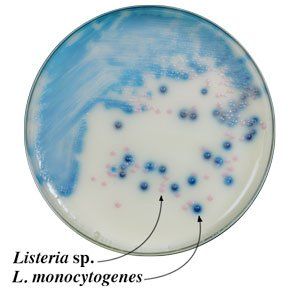
R&F Products
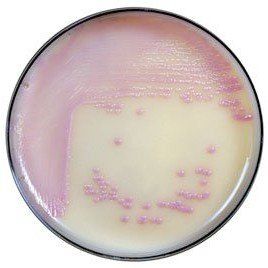
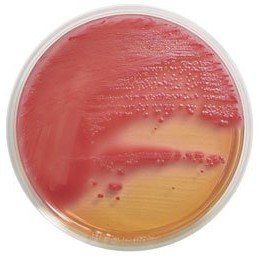
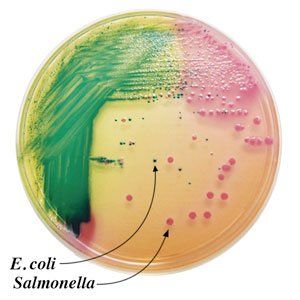
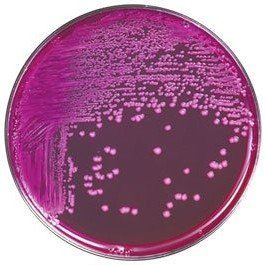
Chromogenic media for the isolation and identification of food pathogens
Flexible shelf life
Powdered chromogenic media and broths provide flexibility to prepare the desired amount of broth and number of plates needed while the unused powder has a shelf life up to 6 years.
Made to order
Full service supply
History
Since 1986, Dr. Lawrence Restaino has been a leader in the development of chromogenic media for the isolation and identification of food pathogens. In 1990, R & F Laboratories was started by Dr. Restaino who quickly realized that the standard plating media and enrichment broths for pathogen isolation was ineffective for operating an efficient laboratory. By 1995, Dr. Restaino started substituting the standard media with newly developed and tested chromogenic plating media which provided a simpler, more innovated approach to detect/enumerate pathogenic bacteria accurately allowing a more efficient and productive laboratory.
News
New R & F® Enrichment Broth Detecton System!
- The R & F® Bacillus cereus Group (BCG) Enrichment Broth was developed to improve enrichment methods for the recovery of Bacillus cereus group species in critical foods, such as powdered infant formula and infant cereal.
- Allows for selective detection when incubated at 30°C for 24-28 h.
- More information can be found here.
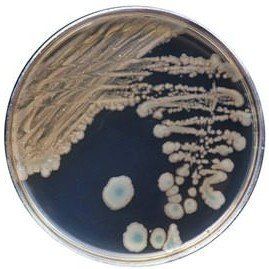
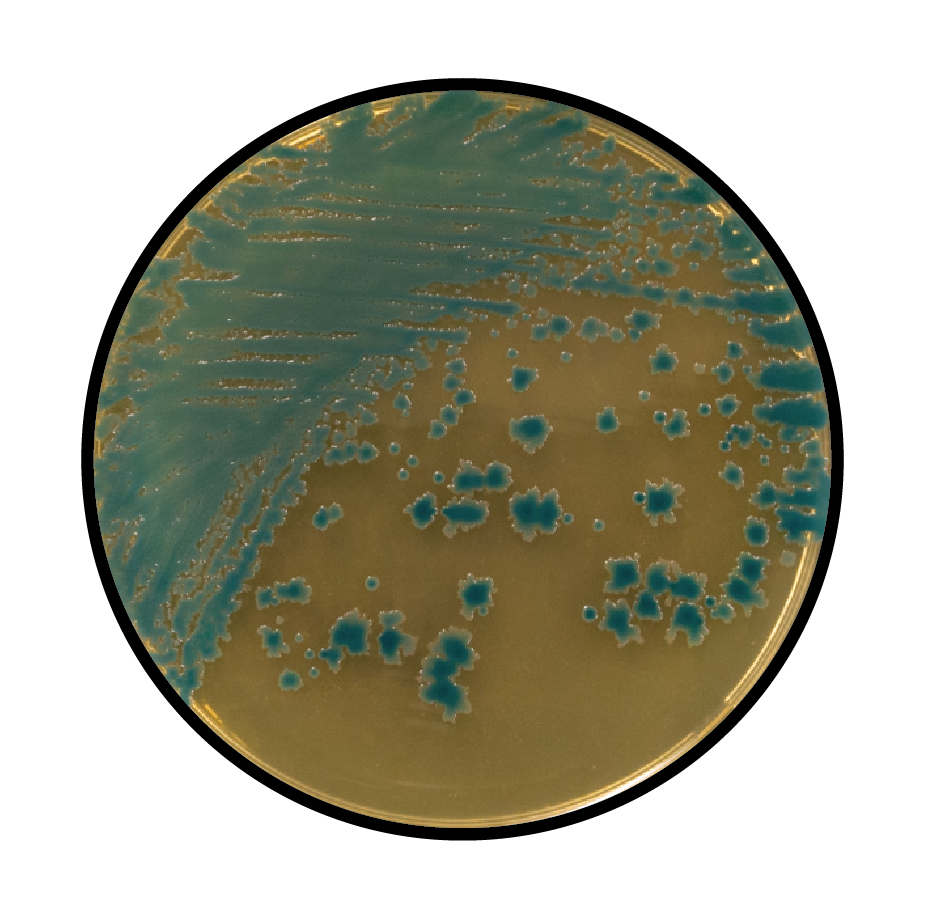
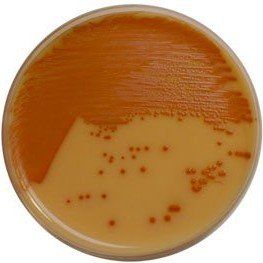
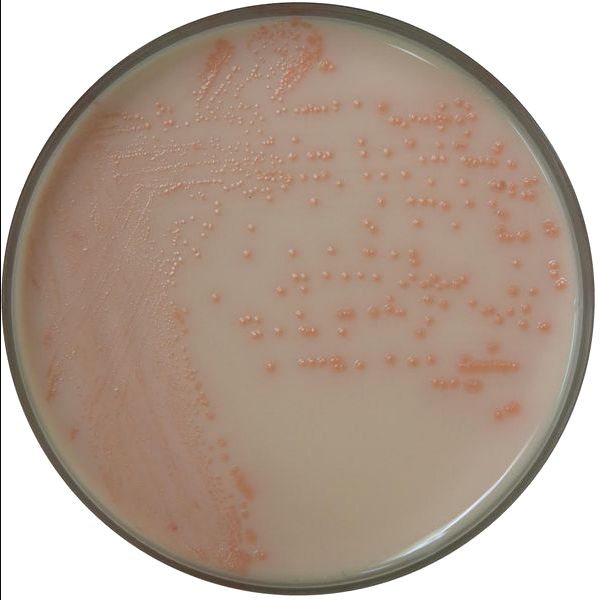
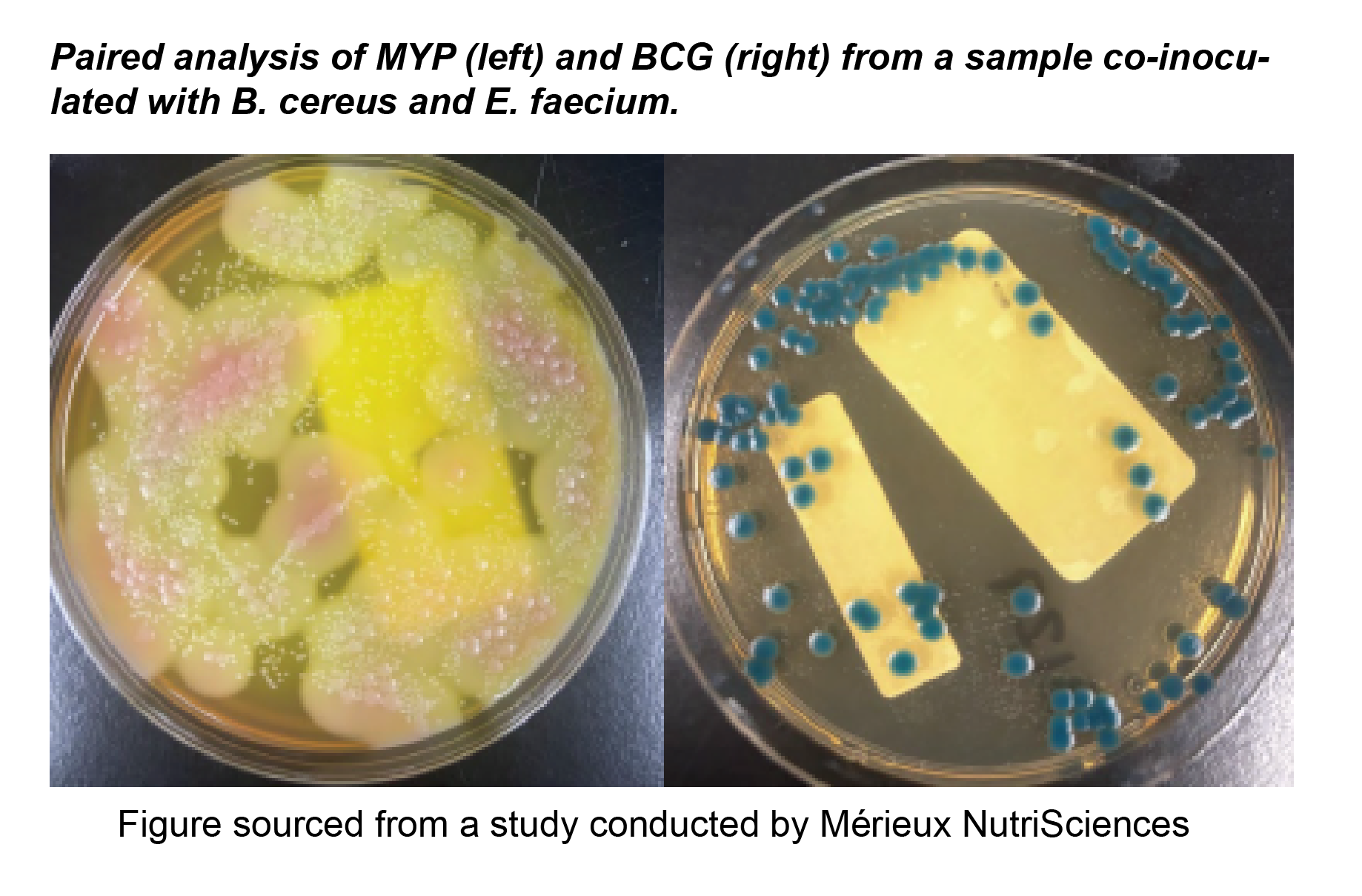
Comparison Study of BCG Chromogenic Media to MYP Agar
- Mérieux NutriSciences conducted a study for R & F® Products comparing the R & F® Bacillus cereus Group (BCG) Chromogenic Agar to Mannitol Yolk Polymyxin (MYP) agar using ISO 7932:2004. Incubation of the BCG agar was performed at two temperatures (30°C and 35°C) across five food items: pasteurized milk, ice cream, potato flakes, rice flour, and powdered infant formula.
- Statistical evaluations confirmed that BCG media remained within acceptability limits. Notably, Bacillus cereus group counts were equivalent to or significantly higher on BCG compared to MYP, depending on the tested food product. Additionally, Bacillus cytotoxicus higher counts were significantly higher on BCG incubated at 35°C than at 30°C.
- Overall BCG enhances sensitivity in detecting B. cereus group species compared to MYP by reducing high background contamination (see figure below).
Changes to the R & F® NRJ-Arcobacter Chromogenic Plating Medium
- The R & F® NRJ-Arcobacter Chromogenic Plating Medium has been reformulated to enhance sensitivity and specificity due to observed growth of high levels of background contamination and reduced recovery of target bacteria. In addition, certain supplement agents have been reduced (i.e., moxalactam and vancomycin) or removed (i.e., cefoperazone and novobiocin). This reformulation is expected to improve the chromogenic medium's performance with no significant changes to the user protocol. Fur further information or questions, please contact us.